
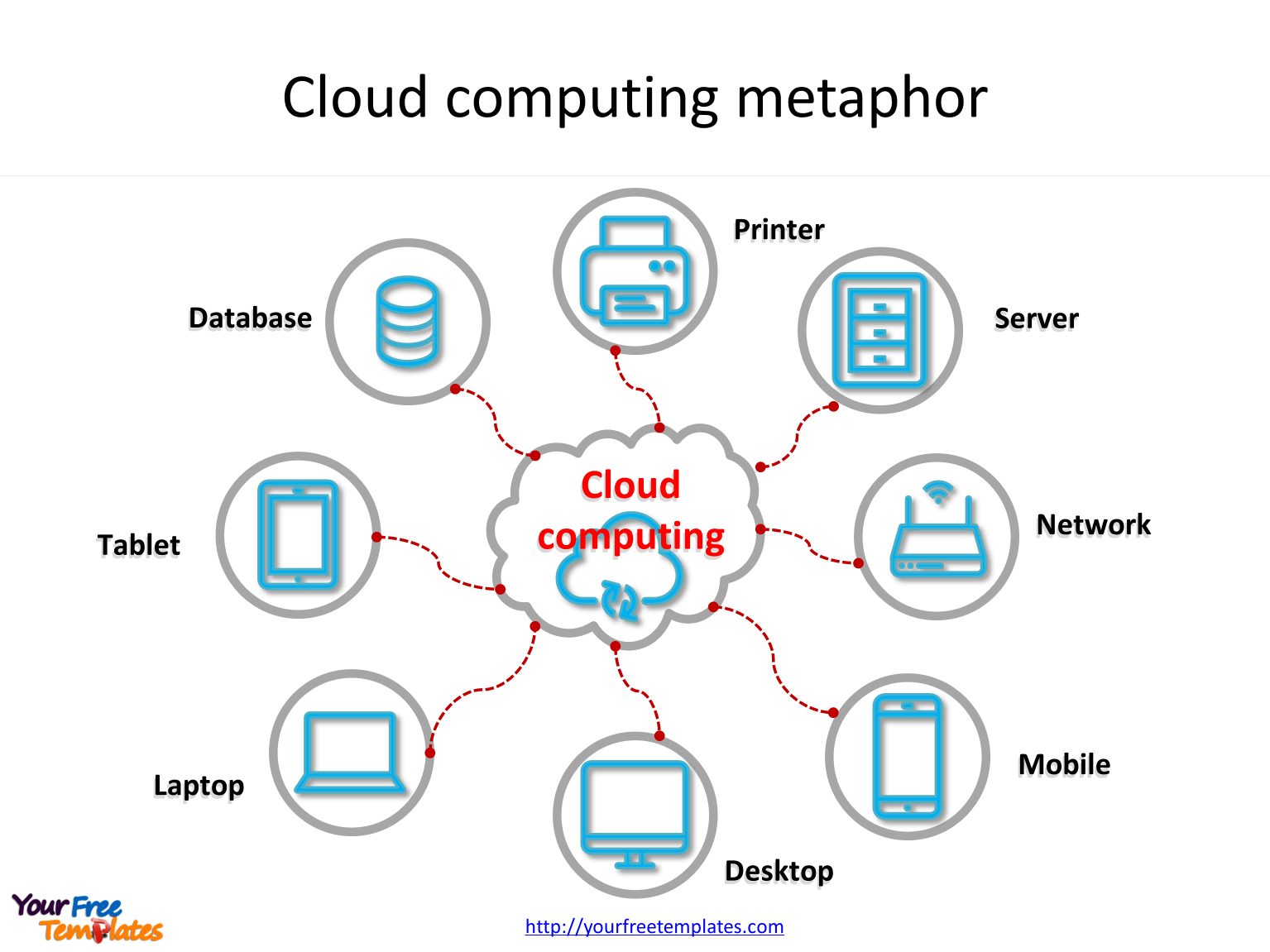
Cloud IT service providers actually provide higher levels of security and data integrity. But today, more people have begun to realize these concerns are misguided.

Ready to learn about the Top 7 Reasons why now is the time to move from on-premise to cloud computing? Cloud enables you to do large-scale business at a lower cost, while improving service quality. But the cloud truly levels the playing field, giving companies of any size the ability to store information at a remote datacenter rather than on-premise. Competition is fierce. Historically, the cloud computing technology used by larger companies was not available to smaller businesses. In the past, only large enterprises had the money to invest in IT infrastructure. Reduce risks, increase upstream visibility, and improve reaction capacity among supply chain components to enable agile sourcing from a variety of suppliers.7 Reasons Why You Should Move from On-Premise to Cloud Computing Blend data from ERP systems handling order management with inventory, warehouse management, and transportation systems.
#Local cloud in cloud computing full#
Retailers can execute a purposeful data strategy to match available inventory to customer demand and increase revenue by optimizing inventory.ĭata from supply chain and enterprise environment related systems such as ERP, EPM, EBS, warehouse and materials planning, or transportation management.Īrchitect a full digital twin for your entire supply chain network to optimize supply chain processes. Improve communication & visibility between stakeholders.Analyze data where it resides & prevent data latency issues.Unify all available data types to better understand how much and where items are across the enterprise.īy sharing data-driven insights across suppliers, warehouses, and stores, retailers can establish a supply chain control tower for automated decision making and AI-based fulfillment. Retail data-inventory, merchandising, warehouse, etc.External variables - weather, incidents, news.Provide a singular platform to bring disparate data sources together for analysis, reporting, and data science to indentify opportunities for improving patient experience. For specific medical conditions, create correlations between diagnosis-treatment-length of inpatient stay-time to return-to-work.Analyze patient segments such as oncology, diabetes, and cardiology.Manage data from healthcare quality, national healthcare safety network, and chronic disease register.FHIR to import large scale clinical data. Meet emerging environmental, social, and governance disclosure requirements. Improve profitability, ensure compliance, and reduce cost of risk.
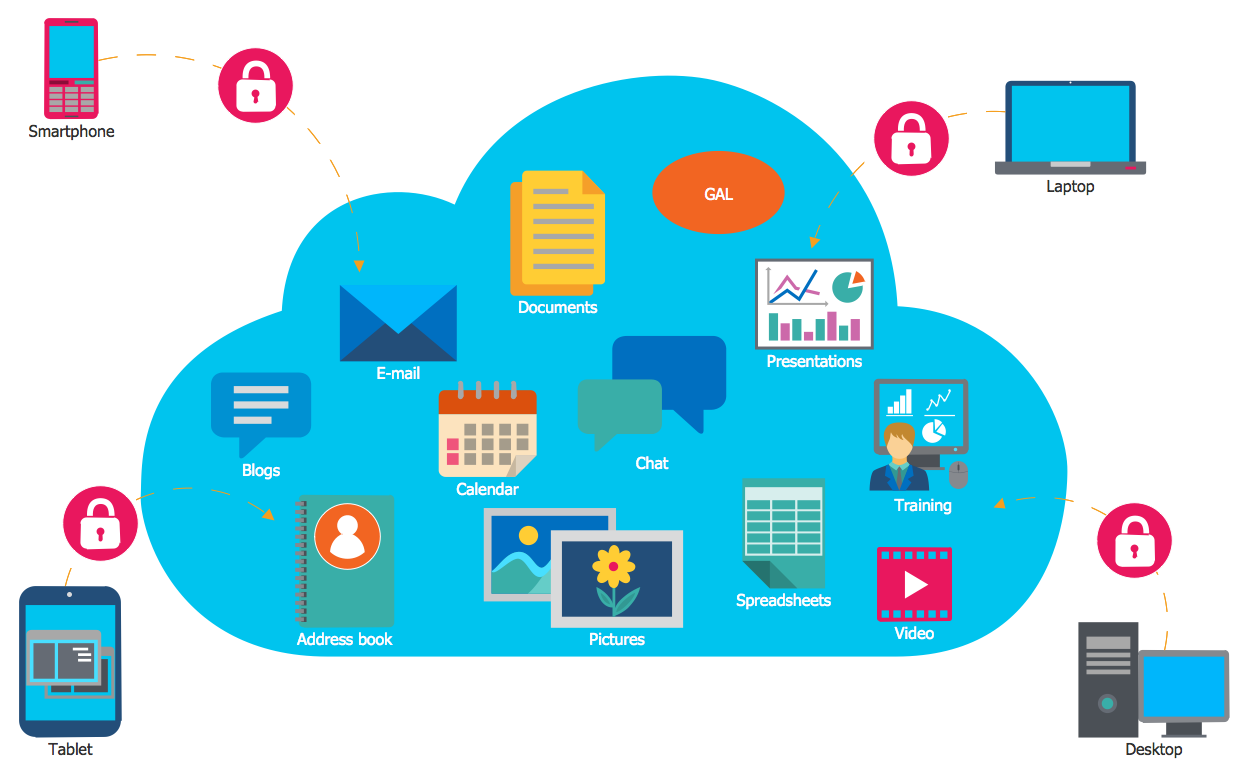
Monitor performance metrics with anomaly detection to spot non-compliance. Apply Monte Carlo and other quantitative risk analysis methods to simulate a range of scenarios with different outcomes and probabilities. Data from both structured and unstructured sources such as systems of record, vendor data, and ATMs.Ĭurate enterprise system data and real-time streaming feeds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
